[:en]
Ransomware is a type of malware designed to encrypt users’ files or lock their operating systems so attackers can demand a ransom payment. According to a 2016 Symantec report, the average ransom demand is almost $700 and “consumers are the most likely victims of ransomware, accounting for 57 percent of all infections between January 2015 and April 2016.”
Similar to a phishing attack, ransomware executes when a user is lured to click on an infected link or e-mail attachment or to download a file or software drive while visiting a rogue website. Sophisticated social engineering techniques are used to entice users to take the desired action; examples include
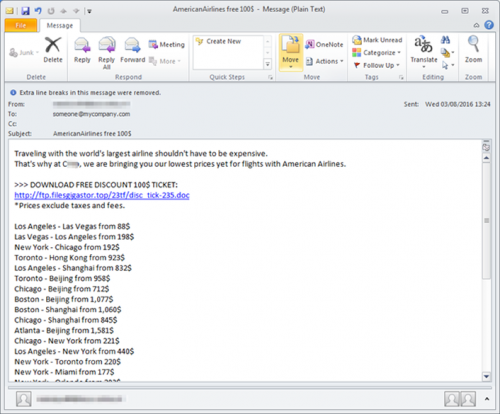
- an embedded malicious link in an e-mail offers a cheap airfare ticket (see figure 1);
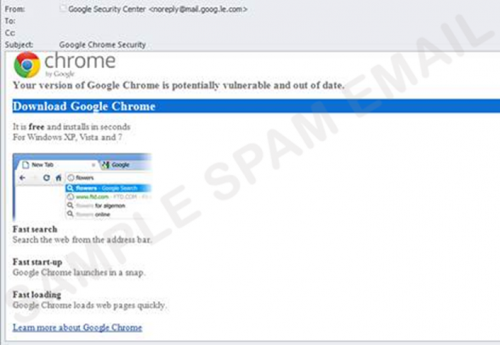
- an e-mail that appears to be from Google Chrome or Facebook invites recipients to click on an image to update their web browser (see figure 2); or
- a well-crafted website mimics a legitimate website and prompts users to download a file or install an update that locks their PC or laptop.
Figure 1. Phishing e-mail with ransomware embedded in a link
Figure 2. A fake Google Chrome e-mail
To avoid becoming a victim of ransomware, users can follow these tips:
- Delete any suspicious e-mail. Messages from unverified sources or from known sources that offer deals that sound too good to be true are most likely malicious (see figure 3). If in doubt, contact the alleged source by phone or by using a known, public e-mail address to verify the message’s authenticity.
- Avoid clicking on unverified e-mail links or attachments. Suspicious links might carry ransomware (such as the CryptoLocker Trojan).
- Use e-mail filtering options whenever possible. E-mail or spam filtering can stop a malicious message from reaching your inbox.
- Install and maintain up-to-date antivirus software. Keeping your operating system updated with the latest virus definitions will ensure that your security software can detect the latest malware variations.
- Update all devices, software, and plug-ins on a regular basis. Check for an operating system, software, and plug-in updates often — or, if possible, set up automatic updates — to minimise the likelihood of someone holding your computer or files for ransom.
- Back up your files. Backup the files on your computer, laptop, or mobile devices frequently so you don’t have to pay the ransom to access locked files.
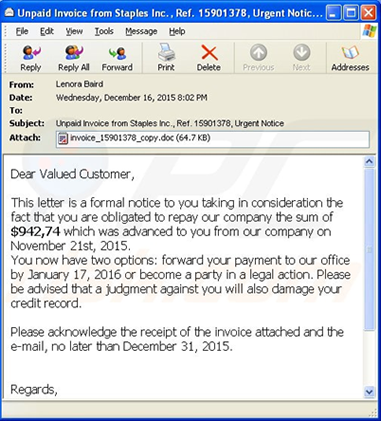
Figure 3. An example ransomware e-mail message
[:af]
Ransomware is `n tipe malware ontwerp om gebruikers se lêers te enkripteer of hulle bedryfstelsels te blok sodat kuberkrakers `n losprys kan eis. Volgens `n 2016 Symantec-verslag, is die gemiddelde losprysbedrag $700 en is 57% van alle sekuriteitsinsidente onder gebruikers tussen January 2015 en April 2016 ransomware.
Soortgelyk aan `n phishing-aanval, lok ransomware ook gebruikers om op `n kwaadwillige skakel te kliek, of `n epos aanhangsel oop te maak of om sagteware af te laai vanaf `n bedrieglike webwerf. Gesofistikeerde sosiale ingenieurswese metodes word gebruik om gebruikers in die versoeking te bring om te reageer, byvoorbeeld
Sophisticated social engineering techniques are used to entice users to take the desired action; examples include
- `n ingesluite kwaadwillige skakel in `n e-pos belowe `n goedkoop vliegtuigkaartjie (siene figuur 1);
- `n e-pos wat lyk asof dit van Google Chrome of Facebook kom nooi ontvangers om op grafika te kliek om hulle webblaaier op te dateer (sien figuur 2); of
- `n goedgeprakseerde webwerf na-aap `n werklike webwerf en por gebruiker aan om `n lêer af te laai of `n opdatering te installeer wat dan hulle toestel sluit.
Figure 1. Phishing e-pos met ransomware versteek in `n skakel
Figure 2. `n Vals Google Chrome e-pos
Om te voorkom dat jy die slagoffer word van ransomware, volg die hierdie wenke:
- Vee enige verdagte e-posse. Boodskappe gestuur vanaf ongeverifieerde bronne wat aanbiedinge bied wat te goed klink om waar te wees, is waarskynlik gevaarlik. (sien figuur 3) As jy twyfel, kontak die beweerde bron telefonies of d.m.v. hulle amptelike adres om die boodskap se geloofwaardigheid te bevestig.
- Moenie op ongeverifieerde e-posskakels of aanhangsels kliek nie. Verdagte skakels kan ransomware (soos die CryptoLocker Trojan bevat).
- Gebruik e-pos filtermetodes wanneer moontlik. E-pos of gemorsposfilters kan keer dat gevaarlike boodskappe in jou posbus beland.
- Installeer en onderhou jou antivirus-sagteware. Hou jou bedryfstelsel op datum met die nuutste virusdefinisies. Dit sal verseker dat jou sekuriteitsagteware die nuutste malware-weergawes kan optel.
- Dateer jou toestelle, sagteware en inprop-programme (plug-ins) gereeld op. Kyk gereeld vir nuwe weergawes of opdaterings van jou bedryfstelsel, sagteware en inprop-programme — of, indien moontlik, stel dat dit outomaties opdateer. Dit sal die kans dat jou rekenaar en data gyselaar gehou word verminder.
- Rugsteun jou lêers. Rugsteun die lêers op jou PC, skootrekenaar en toestelle dikwels sodat jy nie hoef te betaal as jou data nie toeganklik is as gevolg van ransomware nie.

Figuur 3. `n Voorbeeld van `n ransomware e-posboodskap
[:]
Tags: CryptoLocker, phishing, ransomware