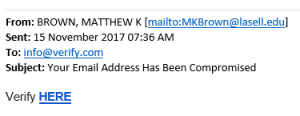
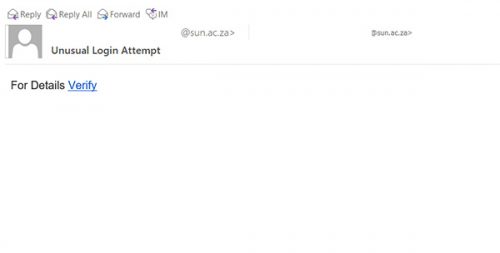
A scam in the form of a well-known “Nigerian 419 Advance Fee” mail is appearing in some of our colleagues and students mailboxes this morning.
The mail is rather simple:
Subject is: “Kindly view attach and forward your reply to <a gmail address>”
The mail’s content simply states the same and the attachment is an image of a letter and states that the sender has a large amount of money that they would like to send you.
This is a typical “Nigerian 411 Advance Fee” scam.
Here is how it works:
You receive an unsolicited message that masquerades as some manner of business proposition, request for assistance, notice of a potential inheritance, or opportunity to help a charity but all of the scam messages share a common theme.
The messages all claim that your help is needed to access a very large sum of money and promise that you will receive a significant portion of this money in exchange for your help.
The scammers use a variety of stories to explain why they need your help to access the funds.
- They may claim that political climate or legal issues preclude them from accessing funds in a foreign bank account and request your help to gain such access.
- They may claim that your last name is the same as that of the deceased person who owned an account and suggests that you act as the next of kin of this person in order to gain access to the account’s funds.
- They may claim that a rich businessman, who has a terminal illness, needs your help to distribute his wealth to charity.
- They may claim that a soldier stationed overseas has discovered a cache of hidden cash left by a fleeing dictator and needs your help to get the money out of the country.
All these scams promise to let you keep a significant percentage of the funds in exchange for your assistance. This is the bait that is used to pull potential victims deeper into the scam. Once a recipient has taken the bait, and initiated a dialogue with the scammers, he or she will soon receive requests for “fees” that the scammer claims are necessary for processing costs, tax and legal fees, bribes to local officials, or other – totally imaginary – fees.
In reality, the supposed funds do not exist and the main purpose of these scam messages is to trick recipients into parting with their money in the form of these advance fees. Fraudulent requests for fees will usually continue until the victim realises he or she is being conned and stops sending money. In some cases, the scammers may gather enough information to access the victim’s bank account directly or steal the victim’s identity.
Typically, advance fee scammers will send many thousands of identical scam messages to recipients all around the world. (as is today’s example) It only takes a few recipients to fall for the claims in the messages to make the operation pay off for the criminals.
What to do if you receive such an Advance Fee email:
It is important that you do not respond to it in any way. The scammers are likely to act upon any response from those they see as potential victims. The best thing to do with these scam messages is to simply delete them.
Send the spam/phishing mail to the following addresses
help@sun.ac.za and sysadm@sun.ac.za.
Attach the phishing or suspicious mail on to the message if possible. There is a good tutorial on how to do this at the following link (Which is safe) : http://stbsp01.stb.sun.ac.za/innov/it/it-help/Wiki%20Pages/Spam%20sysadmin%20Eng.aspx
- Start up a new mail addressed to sysadm@sun.ac.za (CC: help@sun.ac.za)
- Use the Title “SPAM” (without quotes) in the Subject.
- With this New Mail window open, drag the suspicious spam/phishing mail from your Inbox into the New Mail Window. It will attach the mail as an enclosure and a small icon with a light yellow envelope will appear in the attachments section of the New Mail.
- Send the mail.
If you have fallen for the scam:
If you did click on the link of this phishing spam and unwittingly give the scammers your username, e-mail address and password you should immediately go to http://www.sun.ac.za/useradm and change the passwords on ALL your university accounts (making sure the new password is completely different, and is a strong password that will not be easily guessed.) as well as changing the passwords on your social media and private e-mail accounts (especially if you use the same passwords on these accounts.)
IT have set up a website page with useful information on how to report and combat phishing and spam. The address is:
https://blogs.sun.ac.za/it/en/2017/11/reporting-spam-malware-and-phishing/
As you can see the address has a sun.ac.za at the end of the domain name, so it is legitimate. I suggest bookmarking this.
[ARTICLE BY DAVID WILES]