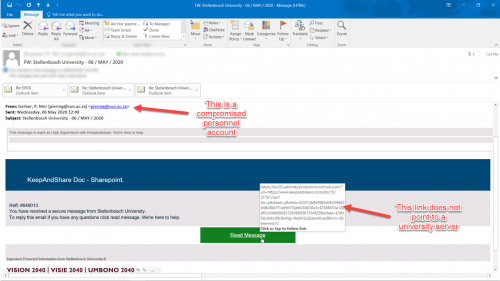
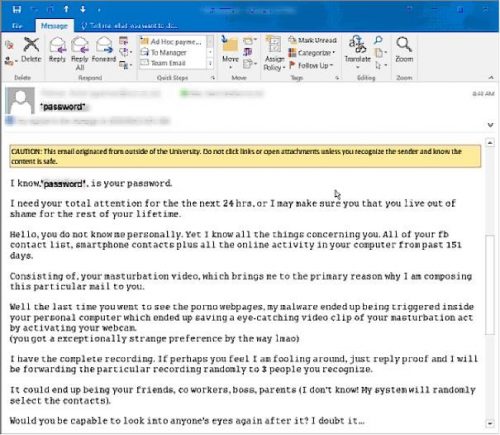
A new potential threat has emerged as we enter the 2nd week of the national lock down and facing the beginning of the new month with bills to be paid.
Phishers are already targeting the South African public with so-called COVID-19 phishing scams, attaching malware infected attachments and encouraging victims to click on a link to download “important information about the COVID-19 pandemic”.
However this week’s scam involves emails, SMS and WhatsApp messages being sent with information about “Payment Relief” from South African banks.
While it is true that most major South African banks are offering payment relief measures to their customers, phishing scammers have grasped this opportunity and adapted their tactics to send emails with content like the following:
“Dear Valued Customer,
“At ABSA Bank, we realise that this is a difficult time for our customers and businesses whose financial means are being negatively affected. After careful consideration and engagements with The Minister of Finance the, Hon. Tito Titus Mboweni, we are pleased to offer you, as a valued customer, a once-off access to a comprehensive relief programme. Please click on the following link to see if you qualify for payment relief.
VERIFY YOUR ACCOUNT
This is a once-off offer made to selected customers and will close at midnight on 2 April 2020.”
This is one such e-mail, but similar scams with forged identities from other South African banks, as well as Whatsapp and SMS messages will also surface. Note the specific deadline and the call to verify your account. Your bank won’t ever ask you to verify your account by email and certainly won’t give you a day to make such a decision.
If you need to make use of a relief programme, rather contact your bank directly than reply to an online message.
Here is a collection of the current verified details for payment relief from South Africa’s 4 major banks:

[ARTICLE BY DAVID WILES]