If you have been using public folders up till now to organise meetings and events in your department, there may be an easier, more practical option available to you.
By sending an email to help@sun.ac.za you can request that the public folders you are using now be converted to resource mailboxes or to request the creation of new resource mailboxes.
But why should you use resource mailboxes instead of public folders?
- If you send a meeting request to a resource mailbox, that resource mailbox will Accept or Decline the meeting request.
- It happens automatically without any intervention of a human being
- You do not have to worry about double bookings for the same date and time at the same venue.
- You’re meeting request to a resource mailbox cannot be changed or deleted.
- Only the owner of the resource mailbox can change or delete meeting requests.
What are public folders?
A public folder is a feature of Microsoft Exchange Server that provides an effective way to collect, organize, and share information with others in an organization. Typically, public folders are used by project teams or user groups to share information on a common area of interest. When you are connected to your Exchange server, folders labelled “Public Folders” appear in the Microsoft Outlook Folder List in the Navigation Pane. You can manage these folders from Outlook. Public folders can contain any type of Outlook folder item such as messages, appointments, contacts, tasks, journal entries, notes, forms, files, and postings. You can also add a shortcut to any public folder to the Favorites folder under Public Folders. (http://office.microsoft.com)
Up till now this is what public folders in Outlook looked like:
 |
 |
| What is a resource mailbox?
A resource mailbox is a mailbox that represents conference rooms and company equipment. Resource mailboxes can be included as resources in meeting requests, providing a simple and efficient way to manage the scheduling of resources for your organization. Room mailboxes are assigned to a meeting location such as a conference room, auditorium, or training room. Equipment mailboxes are assigned to a resource that is not location specific, such as a portable computer projector, microphone, or company car. (http://blogs.technet.com) This is what the new resource mailboxes look like: |
 |
| How do I add a resource mailbox in MS Outlook 2010?
Send an email to help@sun.ac.za and request that the public folders be converted to resource mailboxes. When you get confirmation that it has been done, follow the next steps: Create a new meeting request Select All Rooms in the Address Book |
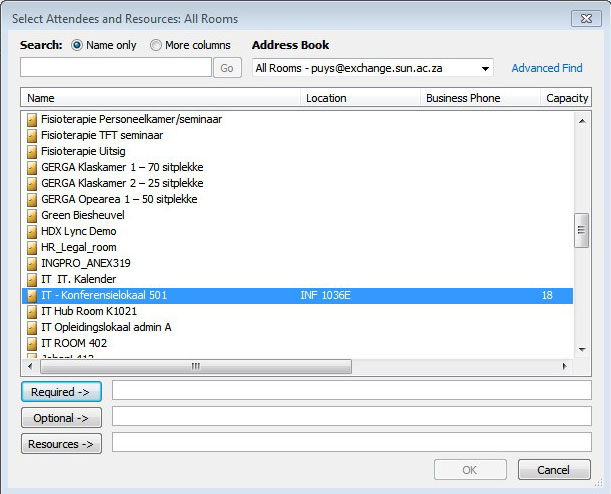 |
| Scroll down to the Room you want to add as a resource mailbox |
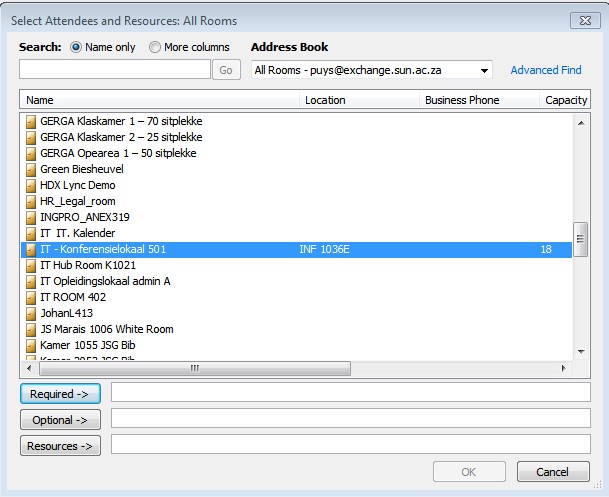 |
| VERY IMPORTANT: Please Take note of the Alias (see the 7th step further down) |
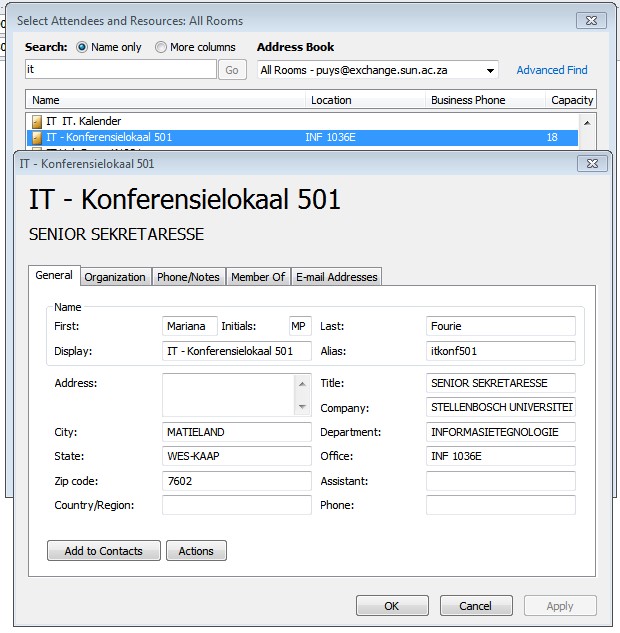 |
| Click on File, Info, Account Settings |
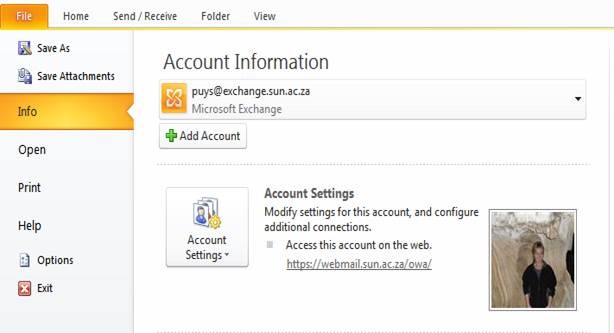 |
| Select your email address and click on Change |
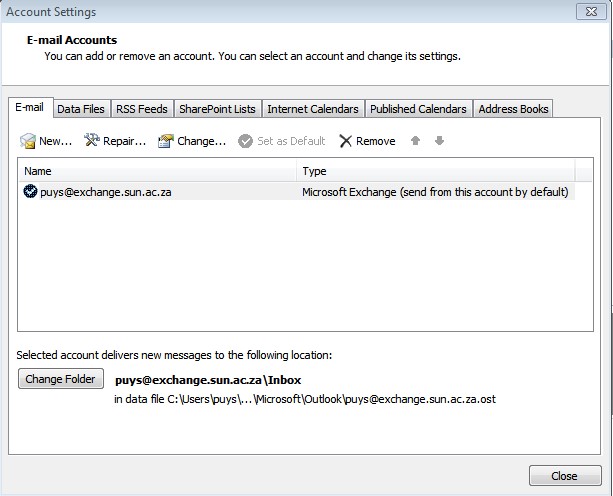 |
| Click on More Settings |
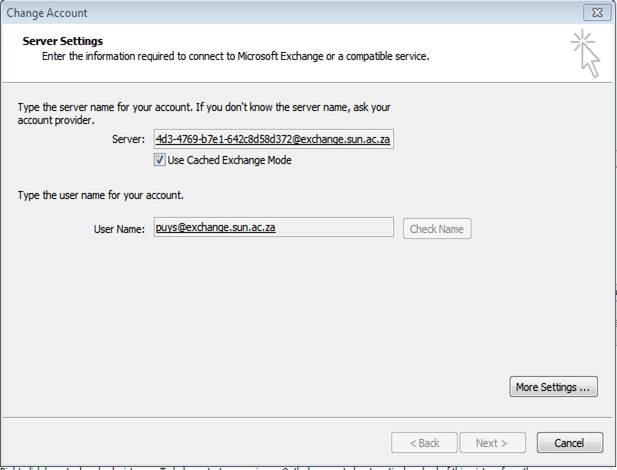 |
| Type the name of the resource mailbox that you want to add – remember that Alias of earlier – it is the name you have to type here |
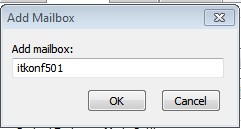 |
| Click Apply, OK, Next Finish |
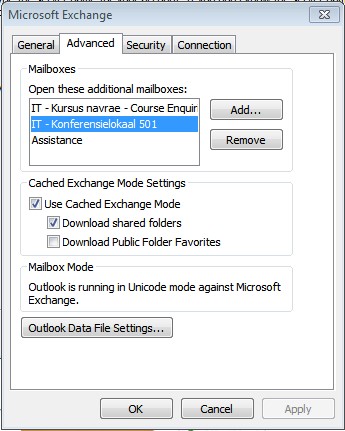 |
| Go back to the Home button and click on Folder List |
| The added Resource Mailbox will display |
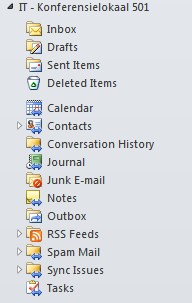 |
| Click on Calendar to view the calendar of the resource mailbox. |


 1. Be concise and to the point
1. Be concise and to the point The School for Public Leadership’s mixed learning project made a leap into the future at the end of February and at the same time highlighted the important role Information Technology plays in modern education and learning.
The School for Public Leadership’s mixed learning project made a leap into the future at the end of February and at the same time highlighted the important role Information Technology plays in modern education and learning.