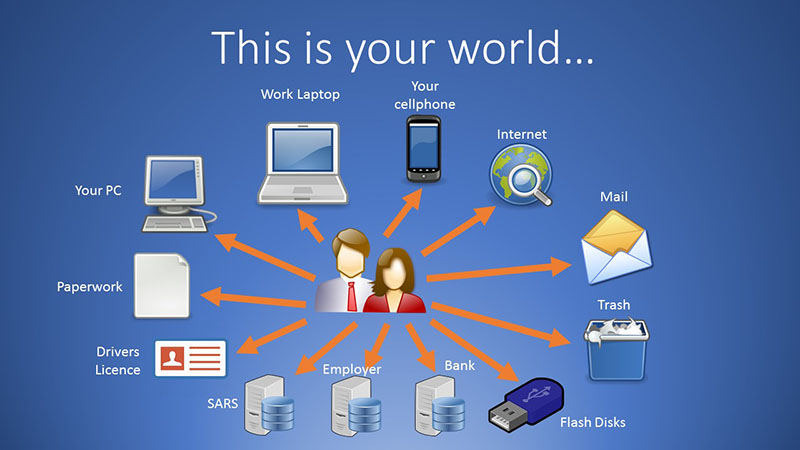
When we use the term “hacker” in our day-to-day conversation, we tend to associate it with an attacker who uses their technical expertise to break into protected computer systems and compromise sensitive data. We hear about this breed of hacker in the news and we invest millions of rands in new technologies to improve our network defences.
When we use the term “hacker” in our day-to-day conversation, we tend to associate it with an attacker who uses their technical expertise to break into protected computer systems and compromise sensitive data. We hear about this breed of hacker in the news and we invest millions of rands in new technologies to improve our network defences.
However, there is another type of attacker who use their tactics to bypass even the most expensive and effective cybersecurity technology. They use a variety of media, including phone calls and social media, and trick people into offering them access to sensitive information. These are the social engineers, hackers who exploit the one weakness found in every institution, also universities: human psychology.┬Ā
Social engineering is a term that covers a broad spectrum of malicious activity. It is a means of attack that leans on human interaction and involves manipulating people. All the methods listed in┬Āour previous article use social engineering.
The object of a social engineer is to convince people to bypass or suppress their natural reserve or suspicion in order to get access to technology systems or data. For example, someone who calls the secretary of a department pretending to be from the IT Department asking questions and getting them to reveal sensitive information such as login names, e-mail addresses, WiFi passwords, etc. They are in essence con-artists.
Whether it is through a phone call or an email, social engineering attacks are always very effective because they rely on the weakest link of security ŌĆō human beings.
The best historical record of social engineering is the story of the Trojan War from Homer’s Illiad. After a ten-year siege on the Trojans, the Greeks pretended to accept their defeat. They left behind an enormous wooden horse as an offer of peace, and the Trojans opened their city gates to bring in the horse as a victory trophy. However, the Greeks soldiers were hiding inside the wooden horse, crept out at night, opened the city gates and allowed the Greek army to enter and destroy the city of Troy.
How to protect yourself:
- First and foremost, be suspicious of anyone who contacts you via email or telephone and appears to know a lot about you. They may be very friendly and attempt to gain your trust, but if youŌĆÖve never dealt with this person before, ask yourself how they know so much about you and why they are contacting you.
- If you are contacted by telephone, donŌĆÖt blindly provide information. If youŌĆÖre suspicious (that little voice in the back of your mind that says “something is not right here”), hang up.
- Offer to call the person back. Ask them for a direct phone number. If they canŌĆÖt provide one, discontinue the call.
- If they do provide a number, do some research. Can you find a website for the company? Do a Google search on the phone number ŌĆō does it come back┬Ālinked to the company name you were given?
As a matter of habit, never give personal or sensitive information, for example, your login name, ID number, password and bank account number, over the phone or email. If the person is persistent, explain that you are concerned about security and will not provide this information over the phone. If they donŌĆÖt accept your explanation, they should not be trusted.
Not only are your inboxes and phone lines being targeted,┬Ābut so are your social media sites. Take a long, hard look at your social media presence. How much do you reveal about yourself to the world? Do you provide information about your position with a company? Do you share your habits ŌĆō where you shop,┬Āgym┬Āor like to eat or socialize? Even the most mundane information you share could make you a target for a social engineering attack. Any social engineer will do their homework on you ahead of time. Whether itŌĆÖs selfies or cat videos, most us like to tweet, tag, link, comment, like, and post online. Platforms like Facebook and Instagram are full of information social engineers can use.┬Ā┬Ā

How many personal details are displayed on your department or Facebook page? Some departmental web pages even display personal cell phone numbers.
Over the past week, there has also been an increase in extortion phishing. Extortion phishing is the practice of obtaining money through force or threats via email. The victim receives an email suggesting they have been recorded through their webcam whilst watching adult websites. The criminals demand a ransom in Bitcoin or some untraceable cryptocurrency and threaten to circulate the recording to their contacts unless payment is made. Often scammers state that they know your password, installed malware on the computer and demand payment.
The new extortion phish threat plays on our own innate sense of guilt. More worrying, however, is that the passwords they have are often correct or close to correct because they have been leaked through data breaches. Usually, these passwords are old and haven’t been used for months or years. In some cases, they’ve remained unchanged or have only changed by a single letter or number. For example, how many times would I have to guess the correct password if the old password is “christopher” and the new password is “Christopher123”.
Your password and email address are potentially out there for all to see.┬ĀOne way to check if your username and password have been leaked in a data breach is to use a site like┬ĀFirefox Monitor. You can enter in your e-mail address and the site will tell you if your information, e.g. email address and password have been compromised.
Social engineering attacks range from unsophisticated attacks, for example simply lying to get information, to very elaborate attacks, for example specifically designed websites. They have one thing in common ŌĆō exploiting the weakest link, human beings.┬Ā
For this reason, these attacks will continue to increase, so being aware and cautious is the best defence.
Next time we will focus a little more on the type of attacks the university has suffered over the past year or so, and how to spot them.
Keep safe out there;