[:en]
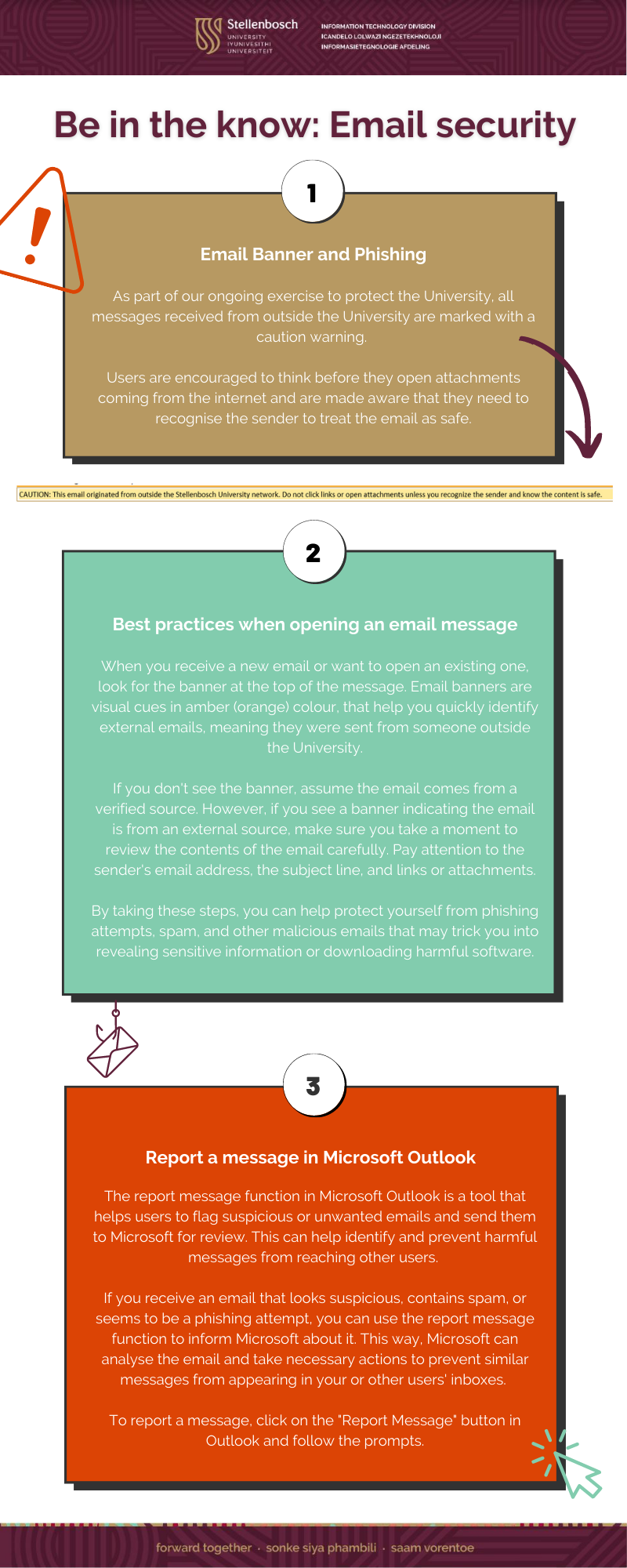
View a PDF here: Phishing and Report Message Infographic
[:]
Tags: phishing
This entry was posted
on Friday, March 31st, 2023 at 6:25 am and is filed under E-mail, General, Internet, Security, Tips.
You can follow any responses to this entry through the RSS 2.0 feed.
Both comments and pings are currently closed.
