We can’t warn you against every phishing e-mailŌĆō there’s a new variation every day. You are the only person who can protect yourself from phishing scams and identity theft. The only way to do this┬Āis to learn to recognise a harmful e-mail by paying attention and keeping an eye out for a few tell-tale signs.
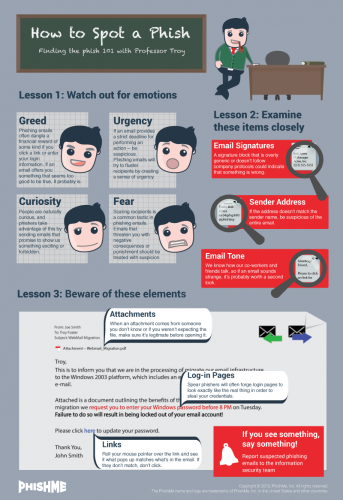 Typical characteristics
Typical characteristics
1. Well-known companies used as bait
These e-mails are sent out to thousands of different e-mail addresses and often the person sending them has no idea who you are.┬ĀIf you have no affiliation with the company the e-mail address is supposedly coming from, it’s fake. For example, if the e-mail is sent by ABSA, but you are a Standard Bank client. Also, see a list of types of companies generally used in phishing e-mails below.
2. Spelling and grammar
Improper spelling and grammar is a dead giveaway. Look for obvious errors.┬Ā
3. Lack of client information
Phishers use a generic greeting. For example, the e-mail greets you as “ABSA customer” or “Dear user”, etc. If the company was sending you information regarding your faulty account, they would mention your account details or name in the e-mail. ┬ĀA company would go through the trouble to address a client by name and won’t ask you for your information. Banks have your information on their system.
4. Deadlines/Sense of urgency
Phishing e-mails demand┬Āan immediate response or stipulate a specific deadline, creating a sense of urgency and prompting you to respond before you’ve looked at the e-mail properly. For example, ┬Ādemanding that you log in and change your┬Āaccount information within 24 hours or your account will be closed.
5. Malicious links
Although many phishing e-mails are getting better at hiding the true URL you are visiting, often these e-mails will show a URL that is unrelated to the company. Move your mouse over the link and look at the display address. Is this the website address of the company who seems to be sending the e-mail? If not, it’s clearly a phishing e-mail.
6. Attachments
Phishing e-mails occasionally include an attachment which contains malware. When opened, it will run and install a small programme on your PC, which hackers use to gain access to your PC and information.┬Ā
Typical phishing topics
ŌĆó Account issues, such as accounts or passwords expiring, accounts being hacked, out-of-date accounts, or account information has to be changed.
ŌĆó Credit cards expiring or being stolen, a duplicate┬Ācredit card, credit card transactions, etc.┬Ā
ŌĆó Confirming orders, requesting that you log in to confirm recent orders or transactions before a delivery can be made.
ŌĆó Winning a prize or getting something for free. Both Woolworths and Pick ‘n Pay’s have been used in fake campaigns to lure people into providing personal details.
Company names phishers generally use
ŌĆó Any major bank. ABSA and Standard Bank are both popular choices in South Africa.
ŌĆó Insurance companies, for example, Outsurance.
ŌĆó Internet service providers
ŌĆó Apple or Microsoft claiming your account has been suspended.
ŌĆó E-mail providers, e.g. Gmail or Yahoo
ŌĆó SARS. Especially at this time of year. (We’ve had a few of these.)
ŌĆó DHL or any delivery company claiming they have a package for you.
ŌĆó┬ĀYour company’s medical aid, for example, Discovery
ŌĆó┬ĀYour company’s IT department
ŌĆó Casinos and lotteries
ŌĆó Online dating websites
ŌĆó Popular websites such as Amazon, Facebook, MySpace, PayPal, eBay, Microsoft, Apple, Hotmail, YouTube, etc.
A few tips to keep you safe
ŌĆó Never follow links in an e-mail you’re uncertain of.┬ĀRather visit the page by typing the address of the┬Ācompany in your browser. For example, ┬Āinstead of clicking on the “ABSA URL” in the e-mail, type http://www.absa.co.za in your web browser and log┬Āin at their official website.
ŌĆó Never send personal information by e-mail. If a company is asking for your personal account information or claiming your┬Āaccount is invalid, visit the website and log in to the account as you normally would. If everything seems in order and there aren’t any urgent notifications from your bank, you should be fine.
ŌĆó If you are still not sure about the status of your account or are concerned about your personal information, contact the company directly, either through┬Āan e-mail address provided on their website, over the phone or visit your local branch.
ŌĆó┬ĀDelete the e-mail and donŌĆÖt click on links or fill in any information.
ŌĆó If youŌĆÖve already divulged your information, immediately change your password or PIN and contact the institution to inform them of the breach.
ŌĆó To report spam or phishing e-mails send an e-mail to┬Āsysadm@sun.ac.za┬Āwith the subject SPAM with the suspect e-mail attached. IT system administrators will then be able to block the e-mail to protect other users.
[SOURCE:┬Āwww.computerhope.com]
 The US government’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency has made a collection of tip sheets available for use. These downloadable PDF documents contain all the information you need to protect yourself from cyber security risks in a convenient, compact format.┬Ā
The US government’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency has made a collection of tip sheets available for use. These downloadable PDF documents contain all the information you need to protect yourself from cyber security risks in a convenient, compact format.┬Ā

 Before
Before