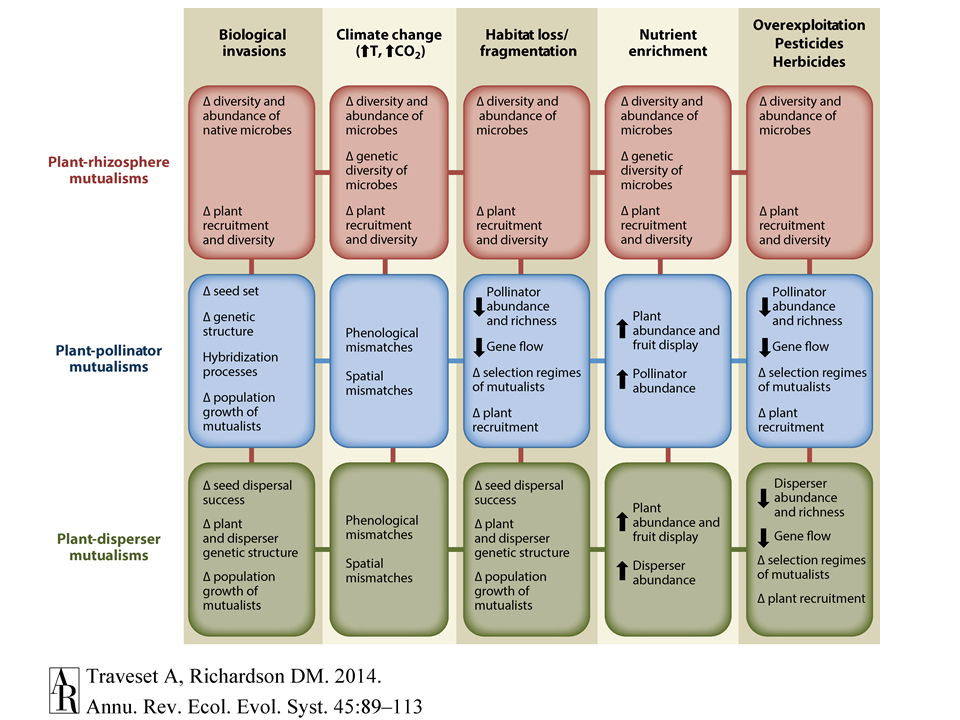
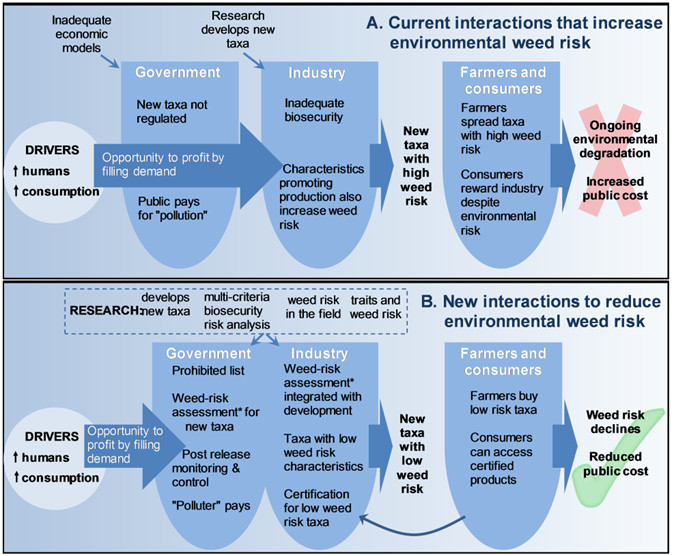
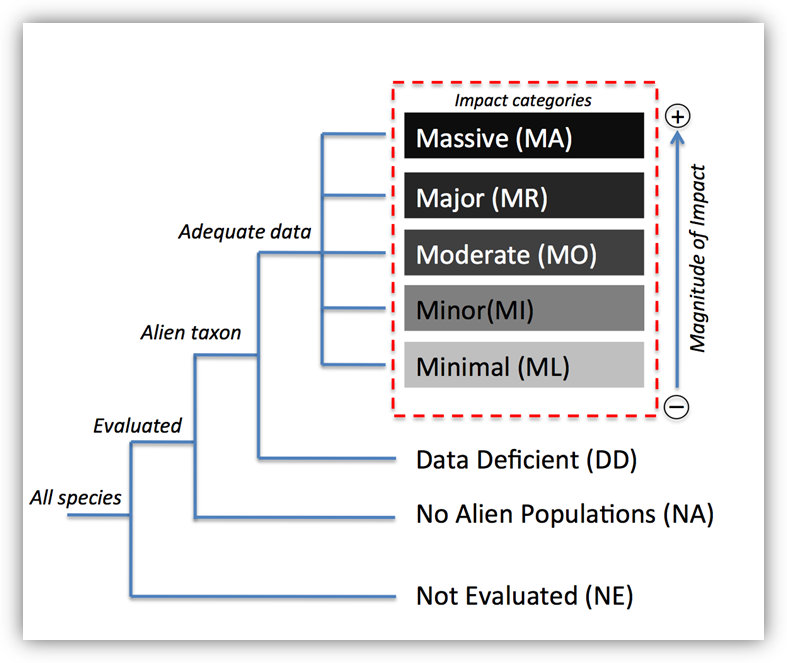
Mutualisms — fundamental mediators of biological invasions
Mutualisms are relationships between organisms of different species in which each individual benefits from the activity of the other. These relationships are hugely important in nature. Essential services provided by mutualists include pollination, seed dispersal and the constitution of global cycles of carbon and other nutrients.