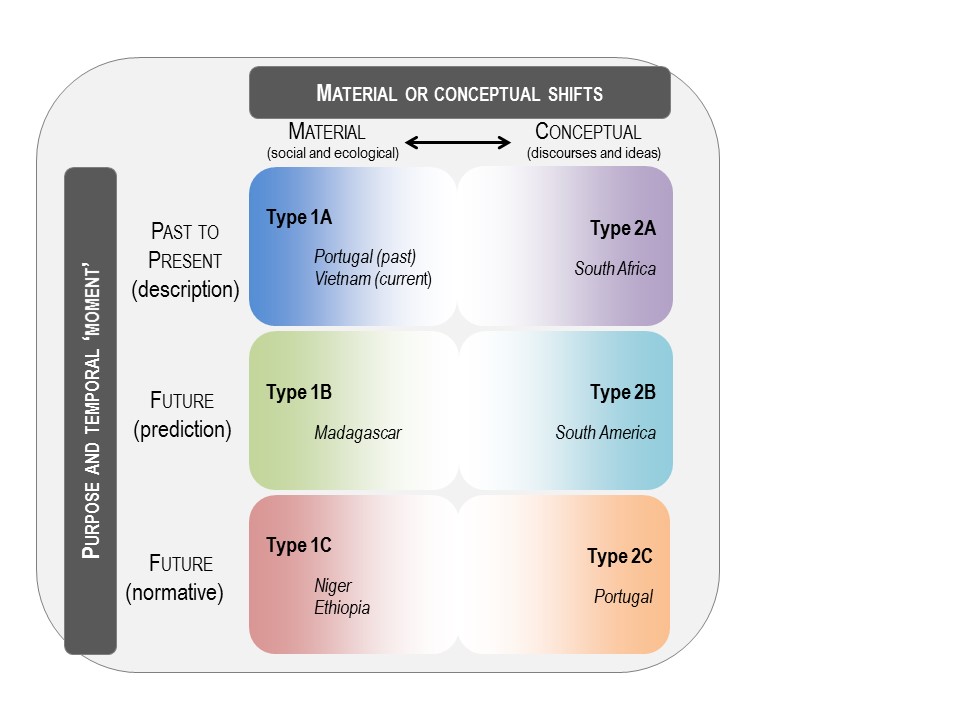
‘Regime shifts’ — a useful concept on which to base discussions about impacts of biological invasions?
What happens when you take a concept developed to describe elements of ecology and apply it to complex social-ecological phenomena involving politics, economics, culture, and more?