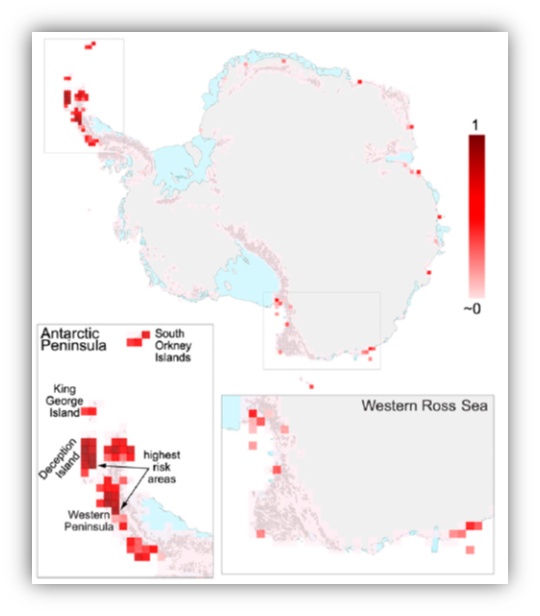
Continent-wide risk assessment for the establishment of alien species in Antarctica
Antarctica is regarded as one of the most pristine environments on Earth. There is, however, a growing concern that the icy continent is being threatened by alien species that are accidentally being brought to the continent in the luggage of tourists and scientists.